Symptoms Causes Of Diabetes Niddk
Diabetes is a number of diseases that involve problems with the hormone insulin. while not everyone with type 2 diabetes is overweight, obesity and lack of physical activity are two of the most common causes of this form of diabetes. it is also responsible for about 90% to 95% of diabetes cases in the united states, according to the cdc. Diabetes types. diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a metabolic disease that causes high blood sugar. the hormone insulin moves sugar from the blood into your cells to be stored or. A small percentage of pregnant women may develop gestational diabetes. its thought that hormones developed in the placenta interfere with the bodys insulin response. this leads to insulin resistance etiology diabetes and high levels of glucose in the blood. Overview type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose) — an important source of fuel for your body.
Diabetes Causes How Do You Get Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes

What causes type 2 diabetes? insulin is a hormone made by your pancreas that acts like a key to let blood sugar into the cells in your body for use as energy. if you have type 2 diabetes, cells don’t respond normally to insulin; this is called insulin resistance. your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Type 2 diabetes can be easy to ignore, especially in the early stages when you're feeling fine. but diabetes affects many major organs, including your heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. controlling your blood sugar levels can help prevent these complications. although long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually, they can eventually be disabling or even life-threatening. some of the potential complications of diabetes include: 1. heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes d This article will give you a better understanding of the causes of type 2 diabetes, what happens in the body when type 2 diabetes occurs, and specific health problems that increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. each section links to more in-depth information on that topic. in a healthy person, the pancreas (an organ behind the stomach) releases insulin to help the body store and use the sugar from the food you eat. diabetes happens when one or more of the following occurs:.
Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. most of the food you eat is broken down into sugar (also called glucose) and released into your bloodstream. when your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. the longer you have diabetes — and the less controlled your blood sugar — the higher the risk of complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: 1. cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosc
What Is Diabetes Cdc


Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs because the body is unable to use blood sugar (glucose) properly. learn more about diabetes causes. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose) — an important source of fuel for your body. with type 2 diabetes, your body either resists the effects of insulin — a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells — or doesn't produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. type 2 diabetes used to be known as adult-onset diabetes, but today more children are being diagnosed with the disorder, probably due to the rise in c Type 2 diabetes is increasingly common worldwide and is beginning to strike younger age groups. almost 90% of all patients with diabetes show insulin resistance, which also precedes the first symptoms of diabetes. the mechanisms underlying the development of insulin resistance are not well understoo. Causes. the exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. usually, the body's own immune system — which normally fights harmful bacteria and viruses — mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing (islet, or islets of langerhans) cells in the pancreas. other possible causes include: genetics; exposure to viruses and other environmental factors.
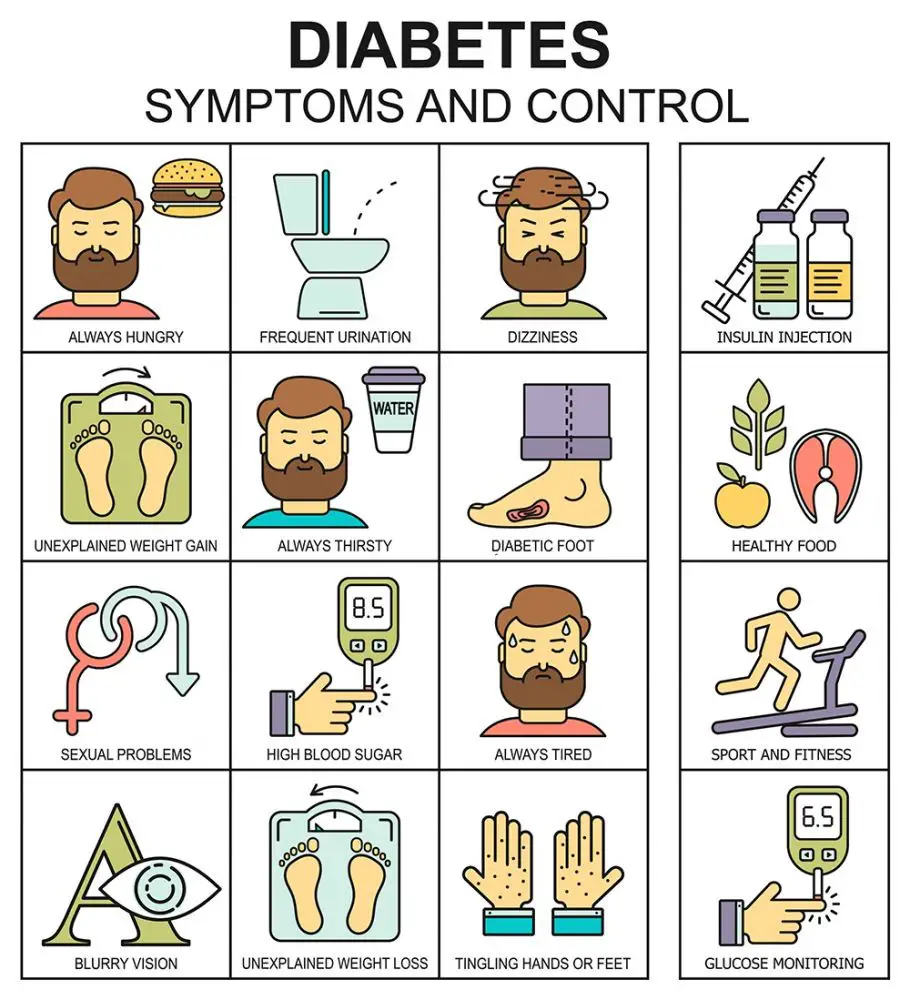
Diabetes symptoms vary depending on how much your blood sugar is elevated. some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, may not experience symptoms initially. in type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly and be more severe. some of the signs and symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are: 1. increased thirst 2. frequent urination 3. extreme hunger 4. unexplained weight loss 5. presence of ketones in the urine (ketones are a byproduct of the breakdown of muscle and Anyone with a body mass index higher than 25 (23 for asian americans), regardless of age, who has additional risk factors, such as high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, a sedentary lifestyle, a history of polycystic ovary syndrome or heart disease, and who has a close relative with diabetes. anyone older than age 45 is advised to receive an initial blood sugar screening, and then. Causes. etiology diabetes type 2 diabetes is primarily the result of two interrelated problems: cells in muscle, fat and the liver become resistant to insulin. because these cells don't interact in a normal way with insulin, they don't take in enough sugar. the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to manage blood sugar levels. Recent genetic mapping and gene-phenotype studies have revealed the genetic architecture of type 1 diabetes. at least ten genes so far can be singled out as strong causal candidates. the known functions of these genes indicate the primary etiological pathways of this disease, including hla class ii.
The etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, niddm) identifies many root causes of this disease, as depicted in the following diagrams. the following diagram is an ishikawa (“fishbone”) diagram that we, as engineers, use to perform root cause analysis. See full list on mayoclinic. org. The causes of diabetes are not known. the following risk factors may increase your chance of getting diabetes: family history of diabetes or a personal history of gestational diabetes. african-american, hispanic, native american, or etiology diabetes asian-american race, pacific islander or ethnic background.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs because the body is unable to use blood sugar (glucose) properly. the exact cause of this malfunction is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors. See full etiology diabetes list on webmd. com.
Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. in fact, you can have type 2 diabetes for years and not know it. look for: 1. increased thirst 2. frequent urination 3. increased hunger 4. unintended weight loss 5. fatigue 6. blurred vision 7. slow-healing sores 8. frequent infections 9. areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck. Women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. according to the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc), women that deliver a baby that weighs more than 9 pounds are also at greater risk. Healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent type 2 diabetes, and that's true even if you have diabetes in your family. if you've already received a diagnosis of diabetes, you can use healthy lifestyle choices to help prevent complications. if you have prediabetes, lifestyle changes can slow or stop the progression to diabetes. a healthy lifestyle includes: 1. eating healthy foods. choose foods lower in fat and calories and higher in fiber. focus on fruits, vegetables and whole grains. 2. gettin The pathophysiology of diabetes is discussed in other chapters; the etiology of diabetes involves a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. “environmental factor” is a broad term that could encompass anything from dietary components to chemical exposures; here the focus will be on environmental pollutants or contaminants.
Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). glucose is vital to your health because it's an important source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. it's also your brain's main source of fuel. the underlying cause of diabetes varies by type. but, no matter what type of diabetes you have, it can lead to excess sugar in your blood. too much sugar in your blood can lead to serious health problems. chronic diabetes con Diabetes is etiology diabetes a chronic disease that occurs because the body is unable to use blood sugar (glucose) properly. the exact cause of this malfunction is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors play a part. risk factors for diabetes include obesity and high levels of cholesterol. some specific causes are discussed below. this is primarily the cause of type 1 diabetes. it occurs when insulin-producing cells are damaged or destroyed and stop producing insulin. insulin is needed to move blood sugar into cells throughout the body. the resulting insulin deficiency leaves too much sugar in the blood and not enough in the cells for energy. this is specific to type 2 diabetes. it occurs when insulin is produced normally in the pancreas, but the body is still unable move glucose into the cells for fuel. at first, the pancreas will create more insulin to overcome the bodys resistance. eventually the cells wear out. at that point the body slows insulin production, leaving too much glucose in the blood. this is known as prediabetes. a person with prediabetes has a blood sugar level higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. unless tested, the person may not be aware, as there are no clear symptoms. type 2 diabetes occurs as insulin production continues to decrease and resistance increases. genetics plays a role in determining how likely you are to develop some type of diabetes. researchers dont fully understand the role of genetics in the development of diabetes. according to the american diabetes association, statistics show that if you have a parent or sibling with diabetes, your odds of developing it yourself increase. genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis and hemochromatosis can both damage the pancreas leading to a higher likelihood of developing diabetes. monogenic forms of diabetes result from single gene mutations. monogenic forms of diabetes are rare, accounting for only 1 to 5 percent of all cases of diabetes found in young people.
Subscribe by Email
Follow Updates Articles from This Blog via Email


No Comments